数据结构——列表
详细介绍见 Josh Hug 为 Berkeley CS61B 编写的教材
基础实现
我们可以创建最基础的链表如下:
public class IntList {
public int first;
public IntList rest;
public IntList(int f, IntList r) {
first = f;
rest = r;
}
/** Return the size of the list using... recursion! */
public int size() {
if (rest == null) {
return 1;
}
return 1 + this.rest.size();
}
/** Return the size of the list using no recursion! */
public int iterativeSize() {
IntList p = this;
int totalSize = 0;
while (p != null) {
totalSize += 1;
p = p.rest;
}
return totalSize;
}
}
如果我们想加入数字 5、10、15,可以采取以下方式:
IntList L = new IntList(5, null);
L.rest = new IntList(10,null);
L.rest.rest = new IntList(15, null);
或者:
IntList L = new IntList(15, null);
L = new IntList(10, L);
L = new IntList(5, L);
int x = L.first;
直观的显示为:
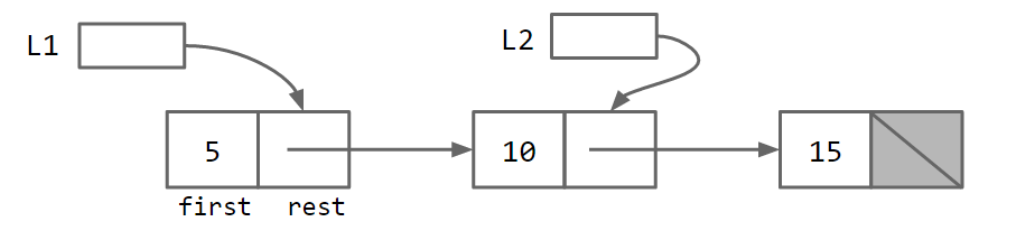
SLList
首先创建列表的单个元素:
public class IntNode {
public int item;
public IntNode next;
public IntNode(int i, IntNode n) {
item = i;
next = n;
}
}
再创建一个类用于与用户交互,简化用户的操作:
public class SLList {
private IntNode first;
public SLList(int x) {
first = new IntNode(x, null);
}
/** Adds an item to the front of the list. */
public void addFirst(int x) {
first = new IntNode(x, first);
}
/** Retrieves the front item from the list. */
public int getFirst() {
return first.item;
}
}
这样处理后的类更易于使用:
SLList L = new SLList(15);
L.addFirst(10);
L.addFirst(5);
int x = L.getFirst();
直观的表示为:
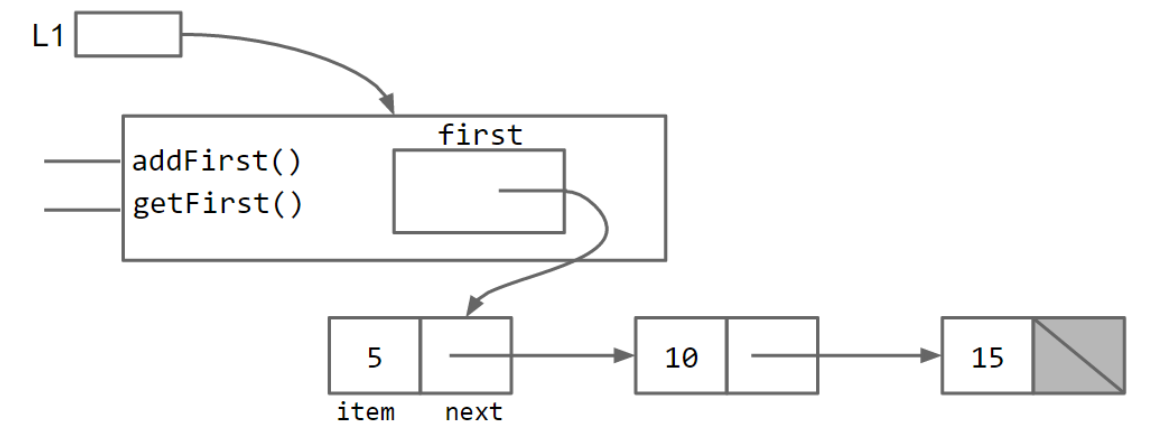
- 进一步,我们可以采用嵌套类整合代码。如果嵌套类不需要使用外层类的任何实例方法和变量,可以将其声明为 static,这意味着静态类中的方法不能访问封闭类的任何成员,在下面代码即表现为 IntNode 中的任何方法都无法访问 first、addFirst 或者 getFirst,这样设置关键词可以节省少量内存。
- 另一个改进是跟踪当前表的 size,这种保存重要数据以加快检索速度的方法有时称为缓存。
- 考虑创建或插入空链表时可能导致的特殊情况(使用 sentinel node)。
public class SLList {
public static class IntNode {
public int item;
public IntNode next;
public IntNode(int i, IntNode n) {
item = i;
next = n;
}
}
private IntNode sentinel;
private int size;
public SLList() {
sentinel = new IntNode(0, null);
size = 0;
}
/**
* Adds an item to the front of the list.
*/
public void addFirst(int x) {
IntNode newNode = new IntNode(x, sentinel.next);
sentienl.next = newNode;
size = 1;
}
/**
* Retrieves the front item from the list.
*/
public int getFirst() {
if (size == 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("List is empty");
}
return sentinel.next.item;
}
/**
* Adds an item to the end of the list.
*/
public void addLast(int x) {
IntNode p = sentinel;
/* Advance p to the end of the list. */
while (p.next != null) {
p = p.next;
}
p.next = new IntNode(x, null);
size += 1;
}
/* common way of calculating size
// Returns the size of the list starting at IntNode p.
private static int size(IntNode p) {
if (p.next == null) {
return 1;
}
return 1 + size(p.next);
}
public int size() {
return size(first);
}
*/
public int size() {
return size;
}
}
DLList
DLList 将是基于 SLList 的改进。改进方向:
- 双向链表,可以降低 addLast 运行耗时,同时解决哨兵节点在链表为空时出现的问题。
- 使用泛型,可以储存任何类型的数据结构
public class DLList<T> {
public static class IntNode<T> {
public IntNode<T> prev;
public int item;
public IntNode<T> next;
public IntNode(T i, IntNode<T> n, IntNode<T> p) {
item = i;
next = n;
prev = p;
}
}
private IntNode<T> sentinel;
private int size;
public DLList() {
sentinel = new IntNode<>(null, null, null);
sentinel.next = sentinel;
sentinel.prev = sentinel;
size = 0;
}
/**
* Adds an item to the front of the list.
*/
public void addFirst(int x) {
IntNode<T> newNode = new IntNode<>(x, sentinel.next, sentinel);
sentinel.next.prev = newNode;
sentinel.next = newNode;
size = 1;
}
/**
* Retrieves the front item from the list.
*/
public int getFirst() {
if (size == 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("List is empty");
}
return sentinel.next.item;
}
/**
* Adds an item to the end of the list.
*/
public void addLast(int x) {
IntNode<T> newNode = new IntNode<>(x, sentinel, sentinel.prev);
sentinel.prev.next = newNode;
sentinel.prev = newNode;
size += 1;
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
}
AList
AList 也是一个可以存储任意长数据的列表,与前面不同的是,它使用数组而非链表,其优势主要在于 get(int i) 即获取特定索引的值的函数的响应时间。
public class AList {
private int[] items;
private int size;
/** Creates an empty list. */
public AList() {
items = new int[100];
size = 0;
}
/** Inserts X into the back of the list. */
public void addLast(int x) {
items[size] = x;
size = size + 1;
}
/** Returns the item from the back of the list. */
public int getLast() {
return items[size - 1];
}
/** Gets the ith item in the list (0 is the front). */
public int get(int i) {
return items[i];
}
/** Returns the number of items in the list. */
public int size() {
return size;
}
/** Deletes item from back of the list and
* returns deleted item. */
public int removeLast() {
int x = getLast();
size = size - 1;
return x;
}
}
该方法的主要难点在于数组的大小调整,做法是创建一个新的数组并复制原数组的内容,但需要考虑到程序用时与内存占用。
具体操作是:
- RFACTOR 为拓展因子,在需要对数组进行拓展时使用乘法拓展;
- THRESHOLD 为触发数组缩小的使用率阈值,即数组中非空部分占比小于此值,对数组进行缩小以减少空间占用;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class AList<T> {
private T[] items;
private int size;
private static final int RFACTOR = 2;
private static final double THRESHOLD = 0.25;
/** Creates an empty list. */
public AList() {
items = (T[]) new Object[100];
size = 0;
}
/** Inserts X into the back of the list. */
public void addLast(T x) {
if (size == items.length) {
resize(size * RFACTOR);
}
items[size] = x;
size += 1;
}
/** Returns the item from the back of the list. */
public T getLast() {
return items[size - 1];
}
/** Gets the ith item in the list (0 is the front). */
public T get(int i) {
return items[i];
}
/** Returns the number of items in the list. */
public int size() {
return size;
}
/** Deletes the item from the back of the list and returns the deleted item. */
public T removeLast() {
T x = getLast();
items[size - 1] = null;
size = size - 1;
// Shrink the array if the size is less than threshold
if (size > 0 && size < items.length * THRESHOLD) {
resize(items.length / 2);
}
return x;
}
/** Resizes the underlying array to the new size. */
private void resize(int capacity) {
T[] newItems = (T[]) new Object[capacity];
System.arraycopy(items, 0, newItems, 0, size);
items = newItems;
}
}


留下评论