数据结构——不相交集
详细介绍见 Josh Hug 为 Berkeley CS61B 编写的教材
简介
如果两个集合没有共同的元素,则称其为不相交集(Disjoint-Sets 或 Union-Find),其数据结构有两个操作:
- connect(x,y):连接 x 和 y,也称 union;
- isConnected(x,y):判断,如果 x 和 y 已连接,返回 true。
在此基础上,我们可以定义我们的 DisjointSets 接口(接口负责决定数据结构应该具有哪些操作):
public interface DisjointSets {
/** connects two items P and Q */
void connect(int p, int q);
/** checks to see if two items are connected */
boolean isConnected(int p, int q);
}
快速查找
考虑使用单个整数数组的方法:
- 数组的索引表示集合的元素;
- 索引处的值是该元素所属集合的编号;
例如,对于{0,1,2,4},{3,5},{6},表示为
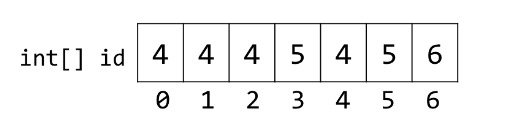
对于这种方法下实现的 isConnected(x,y),我们只需要检查是否有
id[x] == id[y]
这种实现方法称为 Quick Find,因为这样实现下查找元素是否连接需要恒定的时间。具体实现如下:
public class QuickFindDS implements DisjointSets {
private int[] id;
/* Θ(N) */
public QuickFindDS(int N){
id = new int[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++){
id[i] = i;
}
}
/* need to iterate through the array => Θ(N) */
public void connect(int p, int q){
int pid = id[p];
int qid = id[q];
for (int i = 0; i < id.length; i++){
if (id[i] == pid){
id[i] = qid;
}
}
}
/* Θ(1) */
public boolean isConnected(int p, int q){
return (id[p] == id[q]);
}
}
快速联合(Quick Union)
如果我们优先考虑使 connect 操作快速,我们会为每个集合元素分配其父项的索引,如果没有父项,则分配一个负数,这样形成类似一个树结构。
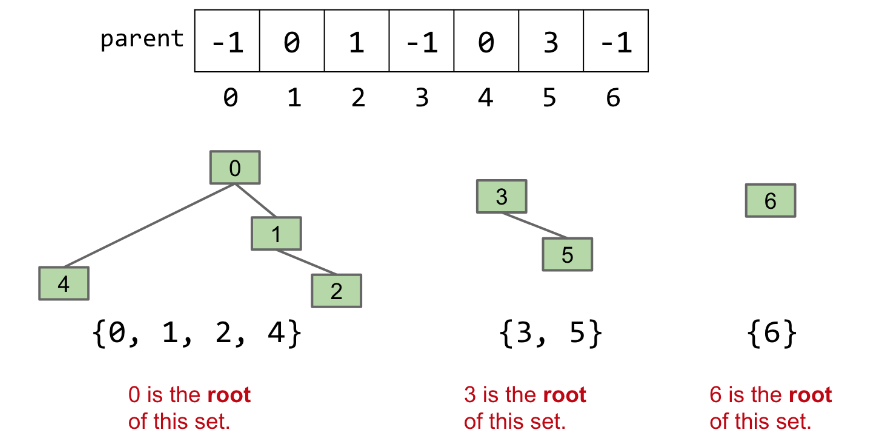
具体实现如下:
public class QuickUnionDS implements DisjointSets {
private int[] parent;
public QuickUnionDS(int num) {
parent = new int[num];
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
}
private int find(int p) {
while (parent[p] >= 0) {
p = parent[p];
}
return p;
}
@Override
public void connect(int p, int q) {
int i = find(p);
int j= find(q);
parent[i] = j;
}
@Override
public boolean isConnected(int p, int q) {
return find(p) == find(q);
}
}
但这种实现仍然存在一个潜在问题,如果树结构过长,find(item)的耗时将变得很大,最坏情况下我们需要遍历所有项目才能到达 root。
两个优化
加权快速联合(Weight Quick Union, WQU)
对 Quick Union 的第一个改进:当我们调用 connect 时,我们将较小的树的根连接到较大的树的根。这样可以保证整体树结构在可能情况下是最矮的,该高度是\(\log(N)\),\(N\)为该Disjoint Sets中的全部元素的数量。
对于最低高度:
考虑两个最基础的只有三个元素构成的树\(T_1\)和\(T_2\),只有当树\(T_1\)被放置在\(T_2\)下面时,树的高度才会加1,拓展一下,当这种情况发生时,结果树的大小至少是\(T_1\)的两倍,因为\(size(T_2)≥size(T_1)\),树\(T_1\)中的元素最多可以被翻倍\(\log_2(N)\)次,直到我们到达\(N\)个元素,每次增加一层高度,即得到最大高度。这种方法与使用树的高度作为合并依据得到的结果是一样的,但是实现更简单。
路径压缩
在 find(x)操作中,我们需要从节点 x 一直遍历到树的根节点。路径压缩的策略是将这一过程中沿途访问的所有节点直接连接到根节点,这样可以显著缩短树的高度,从而提升后续的查找速度,可以使 find 操作的平均运行时间接近常数时间。
优化代码的具体实现如下:
public class UnionFind {
private int[] parent;
private int[] size;
/**
* Creates a UnionFind data structure holding n vertices. Initially, all vertices are in disjoint sets.
*/
public UnionFind(int n) {
if (n <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number of elements must be positive.");
}
parent = new int[n];
size = new int[n];
for (int i = 0;i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
size[i] = 1;
}
}
/**
* Throws an exception if v1 is not a valid index.
*/
public void validate(int v1) {
if (v1 < 0 || v1 >= parent.length) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Index" + v1 + "is not a valid index.");
}
}
/**
* Returns the size of the set v1 belongs to.
*/
public int sizeOf(int v1) {
validate(v1);
return size[find(v1)];
}
/**
* Returns the parent of v1. If v1 is the root of a tree, returns the negative size of the tree for which v1 is the root.
*/
public int parent(int v1) {
validate(v1);
return parent[v1];
}
/**
* Returns true if nodes v1 and v2 are connected.
*/
public boolean connected(int v1, int v2) {
validate(v1);
validate(v2);
return find(v1) == find(v2);
}
/**
* Connects two elements v1 and v2 together. v1 and v2 can be any valid elements, and a union-by-size heuristic is used.
* If the sizes of the sets are equal, tie break by connecting v1’s root to v2’s root.
* Unioning a vertex with itself or vertices that are already connected should not change the sets, but it may alter the
* internal structure of the data structure.
*/
public void union(int v1, int v2) {
validate(v1);
validate(v2);
int root1 = find(v1);
int root2 = find(v2);
if (root1 == root2) return;
if (size[root1] < size[root2]) {
parent[root1] = root2;
size[root2] += size[root1];
} else {
parent[root2] = root1;
size[root1] += size[root2];
}
}
/**
* Returns the root of the set v1 belongs to. Path-compression is employed allowing for fast search-time.
*/
public int find(int v1) {
validate(v1);
if (parent[v1] != v1) {
parent[v1] = find(parent[v1]);
}
return parent[v1];
}
}


留下评论